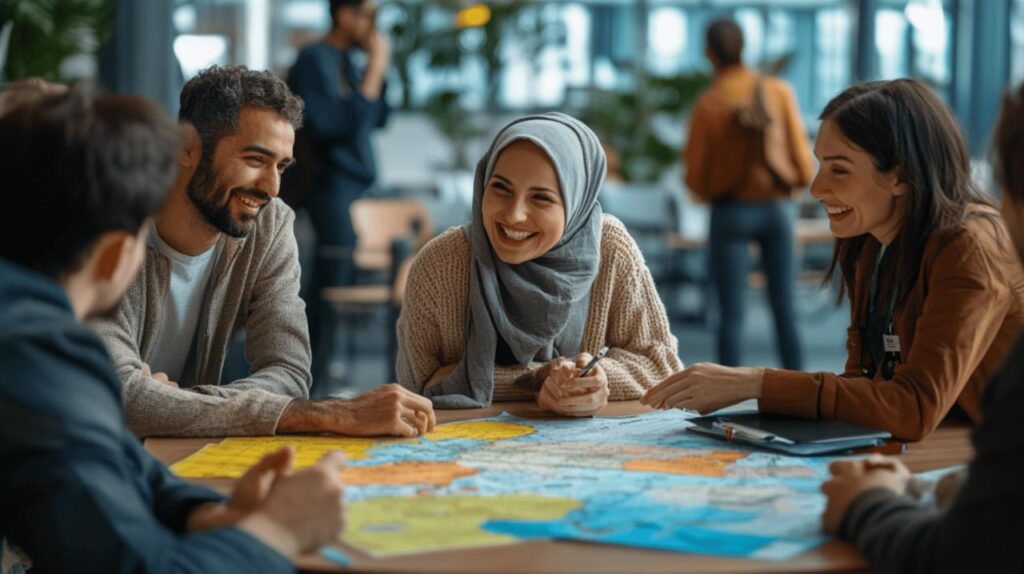
When it comes to navigating the complex landscape of public health, effective communication stands as the cornerstone of successful outcomes. As health challenges evolve in our modern world, so too must the strategies we employ to convey critical health information to diverse populations. The way health messages are crafted, delivered, and received can significantly impact their effectiveness in promoting positive health behaviours and outcomes.
Clear messaging in public health communication
Creating transparent and accessible health communications represents one of the most fundamental aspects of effective public health strategy. Comunica Salud, a leading health communication platform, emphasises that when health professionals employ straightforward language, patient understanding increases dramatically, leading to better adherence to medical advice and improved outcomes. This approach bridges the gap between complex medical knowledge and public comprehension.
Using plain language to maximise understanding
Health literacy varies significantly across populations, making plain language essential for effective communication. When healthcare workers replace technical terminology with everyday words, they ensure that vital health information reaches everyone, regardless of educational background. For instance, instead of referring to ‘myocardial infarction’, using ‘heart attack’ immediately clarifies the condition for most people. This simplification doesn’t diminish the message’s importance but rather enhances its accessibility.
Avoiding technical jargon when addressing the public
Medical terminology serves an important purpose within healthcare settings, but it creates barriers when communicating with the general public. Studies show that excessive jargon correlates with lower patient satisfaction and compromised quality of care. Healthcare professionals must consciously filter out specialised vocabulary when speaking with patients, particularly elderly patients who may feel intimidated by complex medical language. This practice supports patient-centred care and helps establish trust between healthcare providers and recipients.
Tailoring content for target audiences
Effective health communication recognises that different groups have unique needs, concerns, and communication preferences. A message crafted for adolescents about sexual health will require a dramatically different approach than one designed for older adults about managing chronic conditions. Understanding these differences allows health communicators to create resonant messages that inspire action.
Understanding demographic needs and preferences
Demographic factors such as age, socioeconomic status, cultural background, and education level significantly influence how people receive and process health information. Cultural competence in healthcare communication means acknowledging these differences and adapting approaches accordingly. For example, some communities may prefer community gatherings for health discussions, while others might respond better to digital platforms. Health equity depends on recognising these variations and ensuring everyone receives information in ways they can understand and act upon.
Creating age-appropriate health messages
Age represents one of the most crucial factors in tailoring health communications. Children respond to colourful, engaging materials with simple concepts, while adolescents might connect with peer-influenced messaging that acknowledges their growing independence. For elderly patients, considerations around vision, hearing, and digital literacy become essential. Research demonstrates that age-appropriate communication strategies significantly improve patient outcomes and satisfaction across all age groups, making this customisation worth the additional effort.
Brevity and precision in health communications
In our information-saturated world, concise and precise health messages have the greatest impact. When health communicators distil complex information into clear, actionable points, audiences can better absorb and implement the advice. This approach respects the limited time and attention span of most people while ensuring they receive the most crucial information.
Focusing on key information delivery
Health communicators must identify the most essential elements of their message and prioritise these points. When addressing issues like vaccination campaigns or disease prevention, focusing on the core actions required from the public proves more effective than providing exhaustive information. This selective approach helps prevent information overload, which can lead to audience disengagement or confusion about the most important steps to take.
Structuring messages for maximum impact
The structure of health communication significantly influences its effectiveness. Starting with the most critical information, followed by supporting details, ensures that even if someone only reads or listens to part of the message, they capture the essential points. This inverted pyramid approach, combined with clear headings and logical flow, helps audiences navigate health information efficiently, improving comprehension and recall of vital health guidance.
Selecting appropriate communication channels
Even the most perfectly crafted health message fails if it doesn’t reach its intended audience. Choosing the right channels for message delivery represents a critical decision in health communication strategy. The proliferation of communication platforms offers both opportunities and challenges for health communicators seeking to maximise their reach and impact.
Digital platforms for modern health communication
Social media, websites, mobile applications, and other digital channels have transformed how health information circulates. These platforms offer unprecedented reach and targeting capabilities, allowing messages to find specific populations based on demographics, interests, and behaviours. Digital health communication also enables interactivity, allowing audiences to ask questions, share experiences, and engage with content in ways traditional media cannot accommodate. However, digital literacy varies across populations, making this approach most effective when combined with other channels.
Community-based approaches for direct engagement
Despite technological advances, face-to-face communication remains uniquely powerful, particularly for sensitive health topics or communities with limited digital access. Community meetings, health fairs, and direct outreach through trusted local organisations help build trust and provide opportunities for immediate clarification and discussion. These approaches demonstrate respect for community values and create spaces where health concerns can be addressed in culturally appropriate ways, supporting shared decision-making between healthcare providers and community members.
Maintaining message consistency across platforms
When health information varies across different sources, it creates confusion and undermines public trust. Consistency in health messaging across all platforms and materials ensures that audiences receive clear, reinforcing information regardless of where they encounter it. This alignment strengthens message credibility and improves retention of key health information.
Developing core messaging guidelines
Creating central guidelines for all communications about a specific health topic ensures that every piece of content, regardless of format or platform, conveys the same essential information. These guidelines typically include approved terminology, key facts, recommended actions, and messaging priorities. When all communicators work from the same foundation, the resulting consistency helps build public confidence in the information provided, which proves particularly important during health emergencies or when addressing contentious health issues.
Ensuring cohesion between written and visual elements
Visual components of health communication, including images, graphics, and videos, must align with and reinforce written or verbal messages. When visual elements contradict or confuse the written content, they undermine the entire communication effort. Thoughtfully designed visual supports can dramatically improve comprehension, particularly for complex health information or for audiences with limited health literacy. This visual-verbal cohesion creates a more accessible and memorable health message for diverse audiences.
Engaging with public feedback
Effective health communication functions as a dialogue rather than a monologue. Creating mechanisms for the public to respond, ask questions, and share concerns transforms one-way information delivery into meaningful engagement. This approach acknowledges the expertise and agency of community members in their own health decisions.
Creating effective feedback mechanisms
Health communicators must establish accessible channels for audience response, ranging from comment sections on digital platforms to community listening sessions and surveys. These mechanisms should accommodate various communication preferences and abilities, ensuring everyone has an opportunity to contribute. The feedback gathered through these channels provides invaluable insights into how messages are being received, what questions remain unanswered, and what concerns need addressing in future communications.
Responding to community concerns and questions
Collecting feedback represents only half of the engagement process; responding thoughtfully completes the communication loop. When health organisations acknowledge questions and concerns promptly and transparently, they demonstrate respect for their audiences and build trust. This responsiveness shows that public health entities value community input and are committed to addressing real needs rather than simply broadcasting pre-determined messages. Such dialogic approaches significantly enhance patient satisfaction and contribute to improved healthcare experiences.
Evaluating communication effectiveness
Without systematic assessment, health communicators cannot determine whether their strategies achieve the desired impact. Evaluation provides essential data for refining approaches, justifying resource allocation, and demonstrating value to stakeholders. This process transforms communication from an art into a science, allowing for continuous improvement based on evidence rather than assumptions.
Measuring reach and understanding of health messages
Evaluating health communication involves assessing both quantitative metrics like message reach and qualitative factors such as comprehension and attitude change. Tools ranging from analytics platforms to focus groups and surveys help communicators understand who received their messages and how these messages were interpreted. This measurement process reveals whether communications are reaching intended audiences and whether those audiences correctly understand the information provided.
Refining strategies based on performance data
The ultimate purpose of evaluation is improvement. When health communicators analyse performance data, they can identify which approaches work best for specific audiences and topics, allowing for strategic refinement. This evidence-based iteration process ensures that limited resources focus on the most effective strategies and that ineffective approaches are modified or abandoned. This commitment to continuous improvement based on real-world feedback drives innovation in health communication and ultimately leads to better public health outcomes for all communities.